Exact-Match Correlation
Feature
Exact-Match Correlation mechanism allows you to correlate one or more data points from multiple data sources, based on common properties (e.g. Process ID, Thread ID, User Name, etc) to produce a single data point containing merged information from original data sources.
This can be used to “pull together” different pieces of data describing the same event.
Configuration
In this example for Oracle Siebel CRM, we are using Exact-Match Correlation mechanism to correlate all the data that is produced when Siebel application crashes (Event Log file, Crash dump file, FDR file).
The correlation scenario would be set up to generate a single event in Germain to record information from both primary source events.
Go to Germain Workspace > Left Menu > Analytics > Correlation
Click :plus: under Correlation Scenarios
Create a new correlation scenario:
Name – value to be used to configure a KPI to show the correlated data
Retention – how long to keep the correlated data in the cache. In this case, we expect all raw crash data to be received within 1 hour
Type – model type to store correlated data in
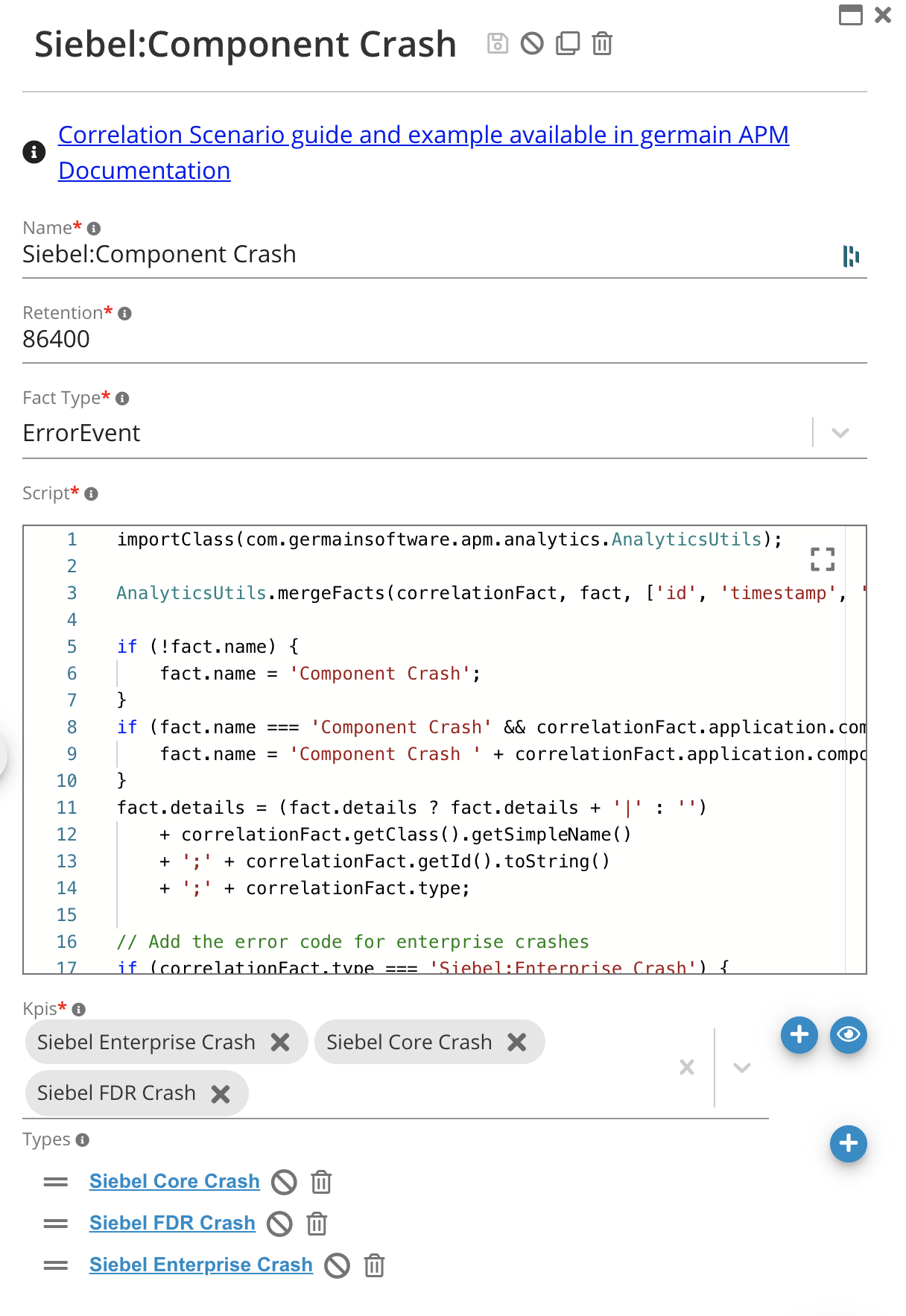
Name Generator – MVEL expression that will populate the “name” field on the correlated data pointSelect the KPIs that will contain the raw data to correlate.
In this example, there are 3 Siebel crash data types that are collected by Germain. Any data point that matches either of the KPIs will be included by the correlation service as part of this scenarioConfigure how incoming KPIs / raw data are correlated.
Name – an identifier to uniquely identify this type
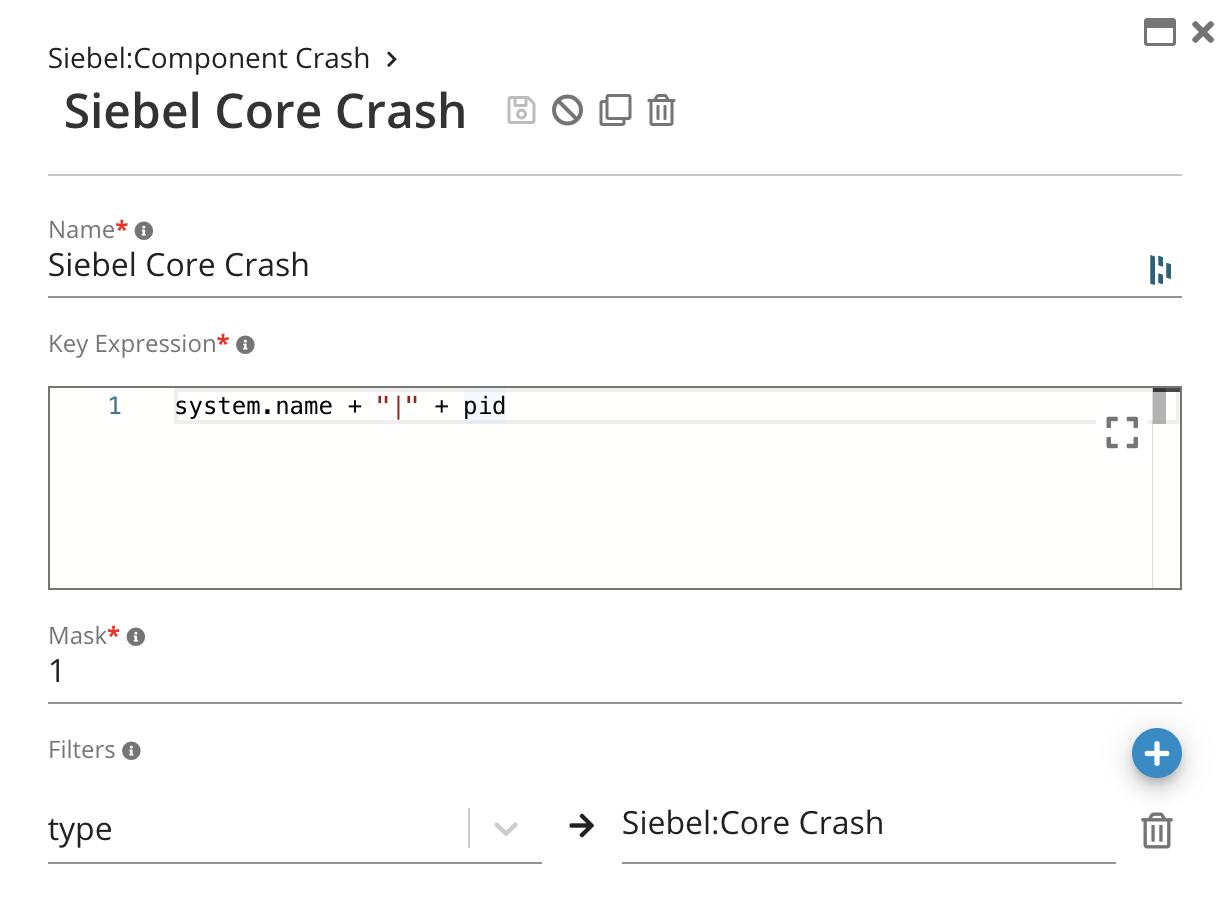
Key Expression – an MVEL expression that will generate a key for this correlation scenario from a raw data point. In this example, the key is comprised of server name and process ID, but other values are possible as well (ex: session ID). Any raw facts that share the same key value will be correlated.
Filters – Specifies filters on the raw data, if any. This makes it possible to assign raw data to a specific correlation type.In this example of a Siebel Crash, we will only define a single type for this purpose
Define which fields to exclude from correlation for the “Crash Event” type. Any fields not included on this list will be copied from the raw data to the correlated fact. For example, since system.name is not included in the list, the correlated fact’s system.name will match the raw facts’ system names.
Once the correlation scenario has been created, the system will begin processing incoming raw data.Creating new KPI
a. Navigate to Analytics → KPIs
b. Create new KPIIn order to visualize the correlated data on a dashboard, create a new KPI that matches the Fact Class and Name properties of the scenario

Component: Engine
Service: Analytics
Feature Availability: 8.6.0 or later
