Categorization
Feature
Germain has the ability to categorize data and events into meaningful groups, enabling the identification of new issues within a large volume of occurrences. This capability is especially useful for detecting previously unseen code exceptions or application crashes—particularly when they involve multiple data sources (e.g., binary files, text files, etc.).
System administrators can easily pinpoint crashes or exceptions that have not been encountered before, allowing them to focus on potential issues that require immediate attention. This proactive approach ensures that emerging problems are addressed quickly, minimizing any negative impact on system performance or user experience.
In summary, Germain’s categorization features significantly enhance error management by helping system administrators:
Analyze the frequency of errors
Reduce the effort required to review issues
Prioritize the resolution of critical problems
Detect new or unique errors automatically
These capabilities streamline the troubleshooting process, leading to faster resolution and improved overall system stability.
Video Overview: https://youtu.be/NaQ_IQRjbU4
AI-Generated Labels for Scripted Categorization
GermainUX now supports AI-generated labels for data categorization when High-Volume data Categorization is required e.g. JavaScript console events. Data is categorized through custom scripts (existing categorization mechanism) that are performant at scale. New labels for these categories can be AI-generated to make them human-readable, improving clarity and reducing manual effort.
AI-Driven Fact Categorization
GermainUX’s fact categorization also supports categorization utilizing one of several LLMs (Large Language Model) most used when Low-Volume Data is involved e.g. User Feedback. GermainUX’s AI service handles the entire categorization process. It uses a customizable prompt to classify and update each fact accordingly.
Examples
Java Exception Categorization
For Java applications, Germain analyzes the full "path" of an exception or failure to differentiate between new and recurring issues. While most APMs simply log another NullPointerException, Germain distinguishes between instances such as:
UserService.getCurrentBusinessLogicService.performLogic
This granularity is essential for managing errors effectively, especially at scale.
Examples:
Java Exception 1 detected by Germain UX:

Java Exception 1 detected by Germain UX
Java Exception 2 detected by Germain UX:
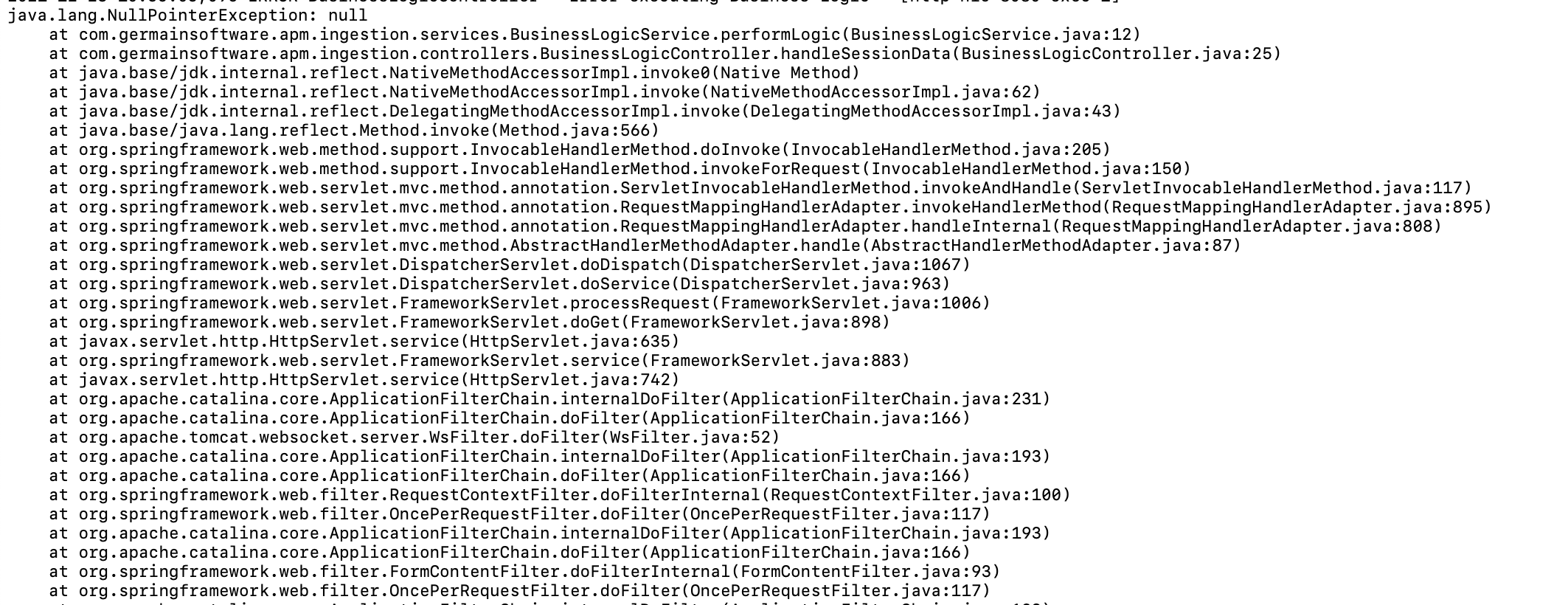
Java Exception 2 detected by Germain UX
Javascript Error Categorization
For web applications built with frameworks like Angular, React, etc., Germain identifies new error types and evaluates their business impact. Unlike most APMs that just report another generic Uncaught TypeError, Germain differentiates between issues like:
...reading ‘toString’......reading 'b'...
This precision helps teams locate and resolve problems more effectively.
Examples
JavaScript Error 1 detected by Germain UX

Javascript Error detected by Germain UX
JavaScript Error 2 detected by Germain UX
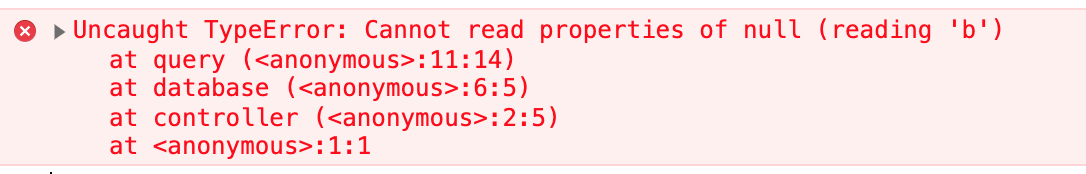
Javascript Error detected by Germain UX
Siebel CRM Object Manager Crash Categorization
For Siebel CRM, analyzing an Object Manager (OM) crash may require parsing several files, including:
Enterprise logs
Object Manager logs
FDR files
Core dump files
Germain streamlines this process by categorizing hundreds of OM crash events into digestible, actionable insights.
Example
A portlet showcasing categorization results for hundreds of Siebel OM crashes.
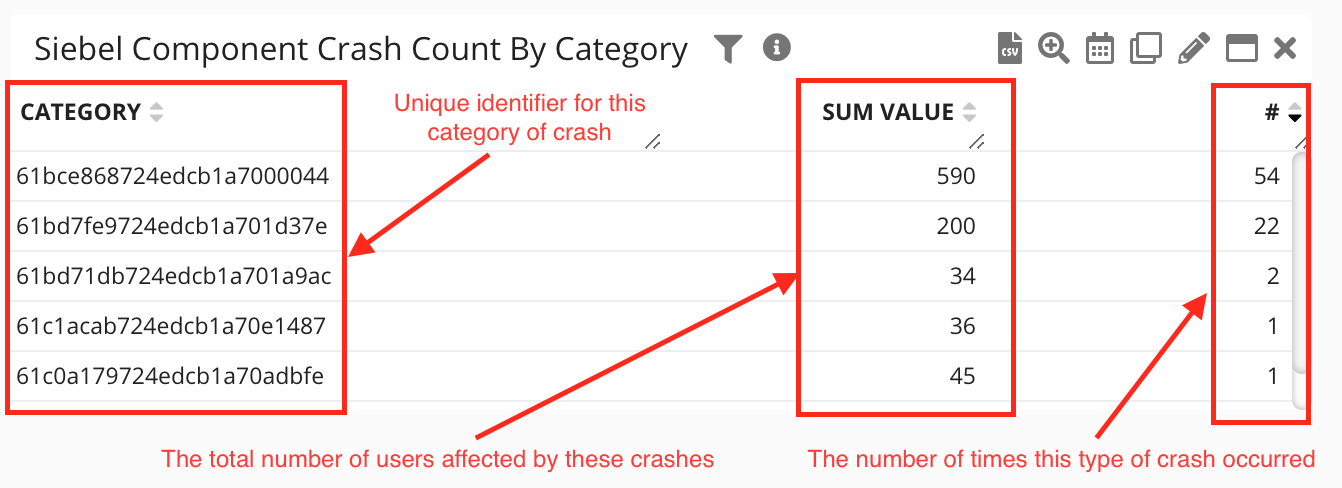
Siebel object manager crashes analyzed by Germain UX
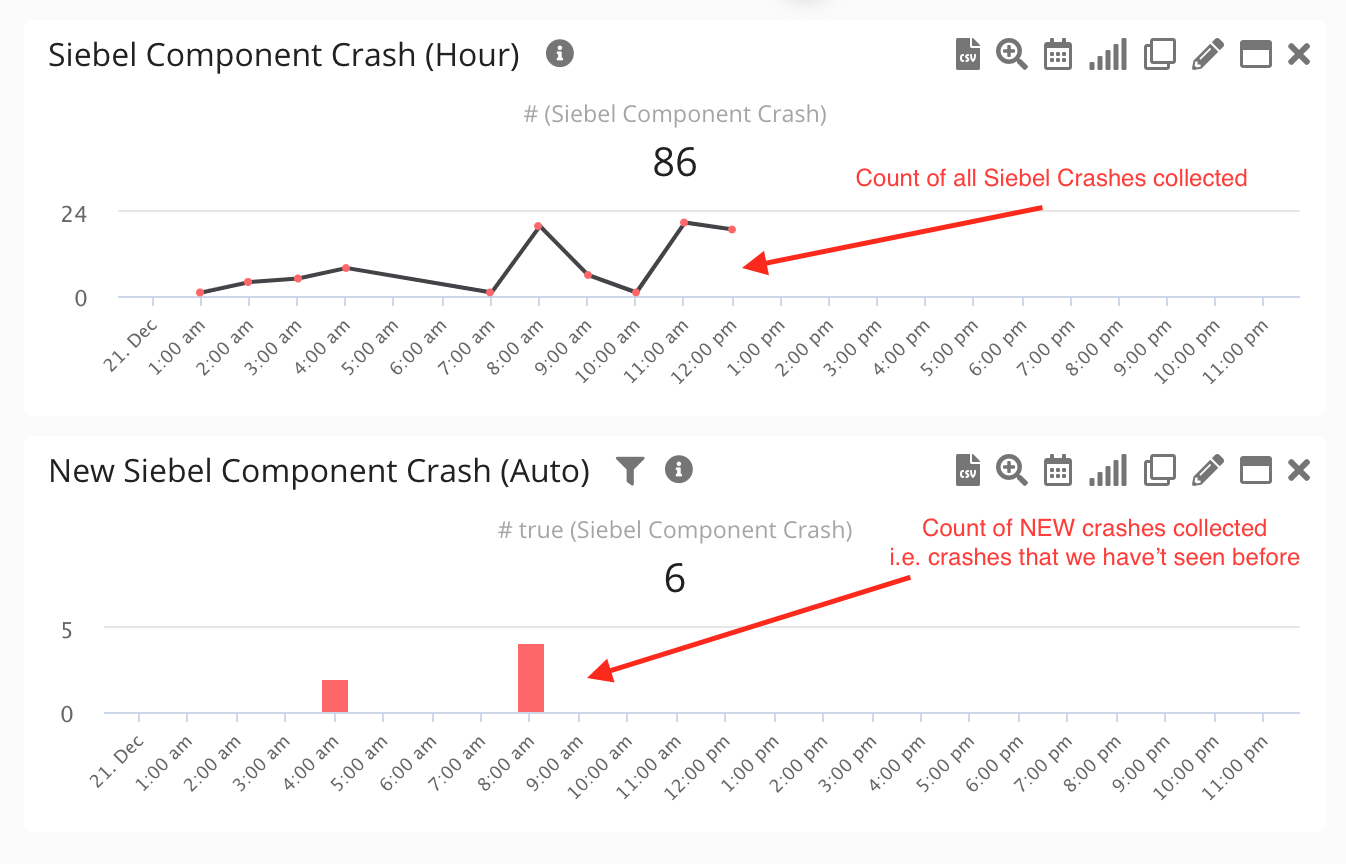
Siebel Object Manager Crash Trend Reported by Germain UX
Drilldown into Siebel crash analysis - Germain UX
Service: Analytics
Feature Availability: 2022.1 or later
