Disaster Recovery
The following steps provide a generic Disaster Recovery plan, intended as a template for planning environment migrations from a Production (PROD) environment to a Recovery/Failover (RECOVERY) environment. As with any template, review and account for specific requirements and special cases before proceeding.
1. Stop All Germain Engines on Production Nodes
2. Update Kafka Url To Point to Recovery Kafka
Login to Germain and navigate to following URL:
<https://<PROD domain>/germainapm/console/s/#germain.apm.monitoringClient.queueConnectors(Kafka)Update the URL field from your PROD Kafka instance to your RECOVERY instance.
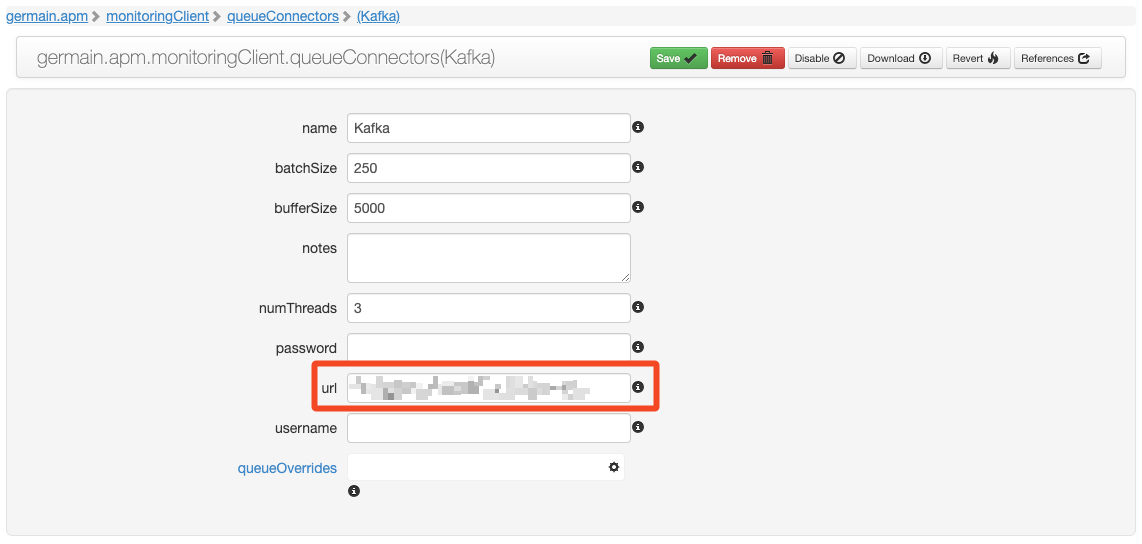
Kafka connector configuration - Germain UX
3. Stop All Germain Services on Prod Nodes
4. Validate All the Infrastructure Services Are Running As Expected on Recovery
Kafka
Zookeeper
Hazelcast
ElasticSearch
5. Start All Germain Services on Recovery Nodes
6. Start All Germain Engines on Recovery Nodes
IMPORTANT steps to take BEFORE starting the engines
Remove the session.txt file from each engine node before starting.
Modify the hostname from the Germain state screen of all nodes before starting. (From PROD to RECOVERY; eg. PROD_***** to RECV_*****)
